“Measuring Neural Responses to Audiovisual Speech Processing During Movie Viewing Using Optical Neuroimaging” – Jonathan Peelle
ARO – February 2023
Images of positive aging from the Centre for Ageing Better's age-positive image gallery (CC0 license).
Key papers from talk
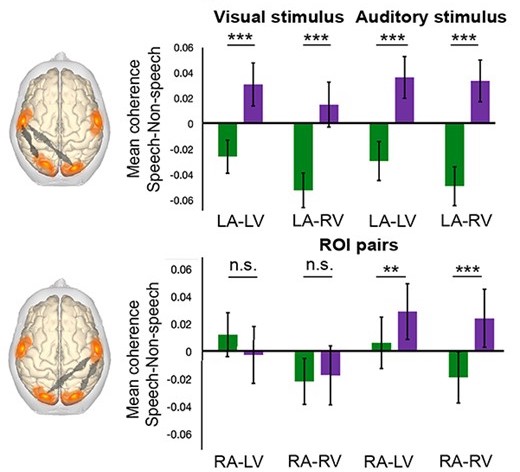
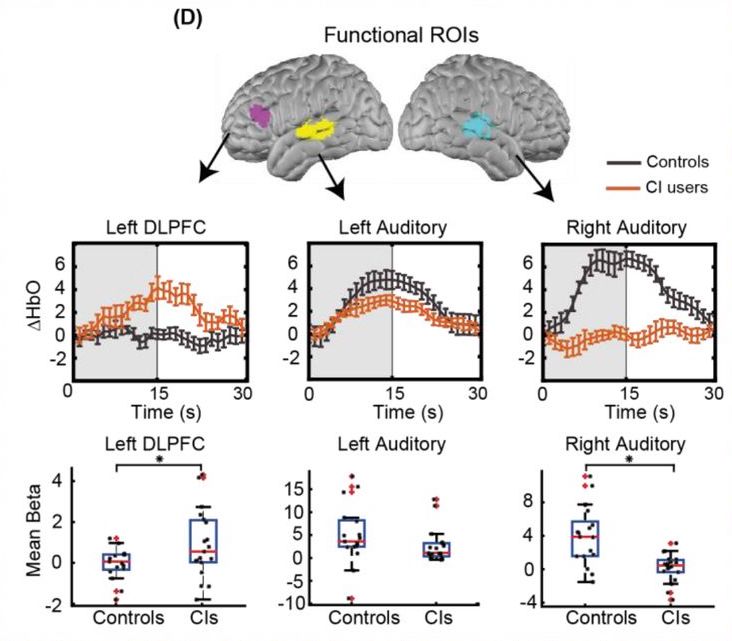
Fullerton AM, Vickers DA, Luke R, Billing AN, McAlpine D, Hernandez‐Perez H, Peelle JE, Monaghan JJM, McMahon CM (In press) Cross‐modal functional connectivity supports successful speech understanding in listeners with cochlear implants. Cerebral Cortex. [html]
Functional connectivity differs depending on both task and population (CI vs. normal-hearing controls).
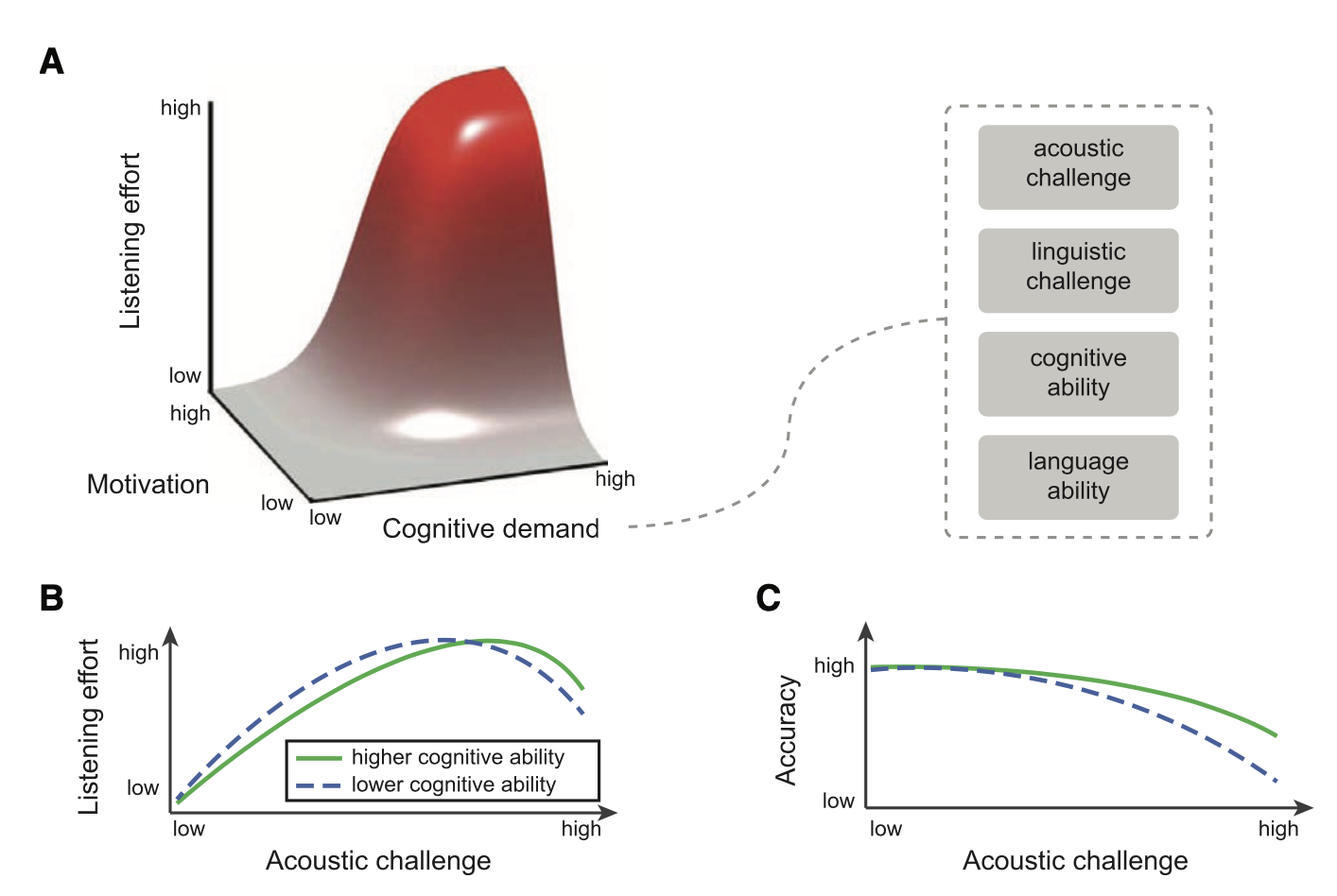
Peelle JE (2018) Listening effort: How the cognitive consequences of acoustic challenge are reflected in brain and behavior. Ear and Hearing 39:204–214. [html] [pdf]
An overview of the background of studies supporting cognitive demands when speech is acoustically challenging.
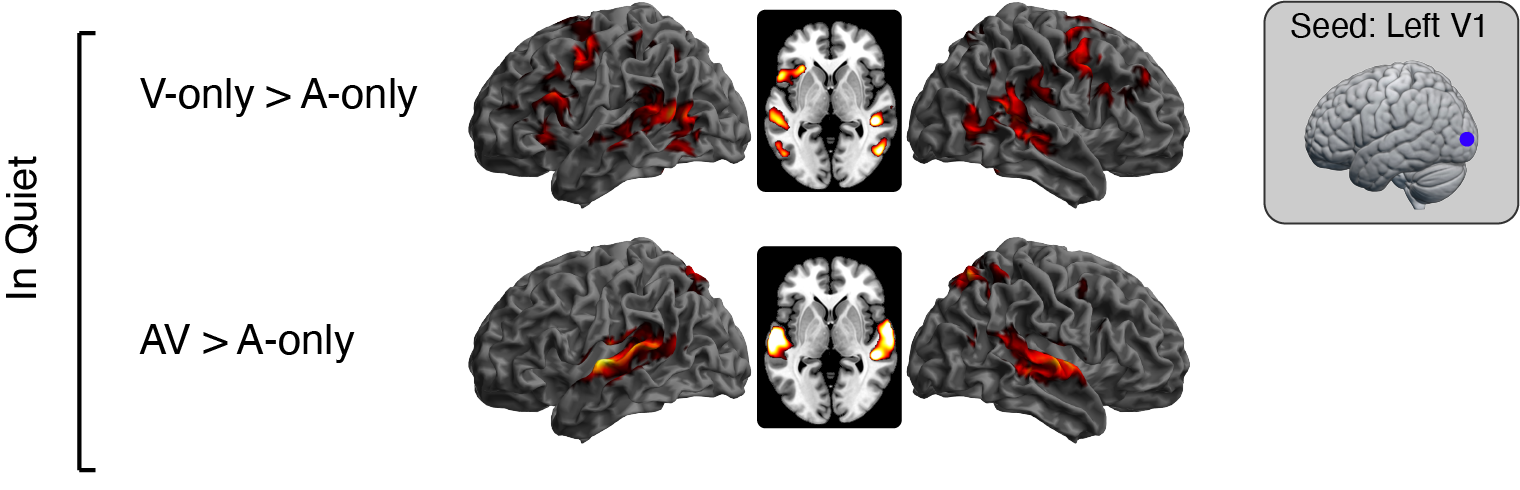
Peelle JE, Spehar B, Jones MS, McConkey S, Myerson J, Hale S, Sommers MS, Tye-Murray N (2022) Increased connectivity among sensory and motor regions during visual and audiovisual speech perception. Journal of Neuroscience 42:435–442. [html]
In a single word paradigm, we used fMRI to study responses to audiovisual and visual-only speech. We found not only different regions responding to audiovisual speech, but differences in effective connectivity for audiovisual relative to unimodal speech, highlighting the importance of interregional coordination in multisensory processing.
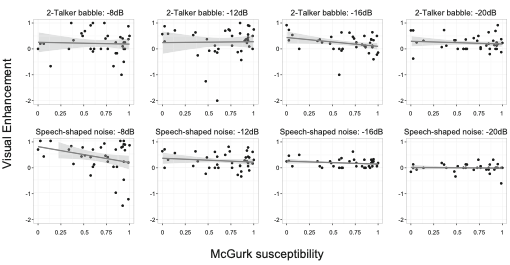
Van Engen KJ, Dey A, Sommers MS, Peelle JE. Audiovisual speech perception: Moving beyond McGurk. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 152:3216–3225. [html]
In this opinion paper on audiovisual speech processing we discuss the (in)famous McGurk effect, arguing that McGurk stimuli are not the best for studying natural audiovisual speech perception.
Sherafati A, Dwyer N, Bajracharya A, Hassanpour MS, Eggebrecht AT, Firszt JB, Culver JP, Peelle JE (2022) Prefrontal cortex supports speech perception in listeners with cochlear implants. eLife 11:e75323. [html]
Using optical neuroimaging we show increased activity in DLPFC in listeners with cochlear implants when listening to speech compared to controls.
Me, elsewhere
- Publications
- Lab website: peellelab.org
- follow me on Mastodon